Chatbot wars are gearing up for full throttle – with Microsoft, Google, and potentially Apple leading the race. Microsoft-backed OpenAI has the first-mover lead in the arms race with the fastest growing tool ever. But Google and Apple also have massive amounts of data and billions of dollars to eventually equal or surpass OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
All of these chatbots use generative AI – a type of artificial intelligence that can simulate conversations and the written word by doing the thinking for you, faster than a Human, and provides detailed responses to questions for queries. It works by learned patterns from data it has been trained on.
Generative AI can be used to produce a wide range of outputs, including text, images, music, and more. And this is also where malicious intent through mostly Business Email Compromise (BEC) enters the equation.
Let’s take a quick, high-level look at ChatGPT and its generative AI qualities in terms of malicious intent. Let’s start with the bottom line – threat actors today are currently using ChatGPT to launch cyberattacks. ChatGPT allows these threat actors to increase the speed and variation of their attacks by modifying code in malware or creating thousands of variations of social engineering (again BEC) attacks to increase the probability of success. These are the first steps. As machine learning (ML) advances with use, so will the variety of ways it can be applied for malicious intent.
Here are some examples of malicious use:
- The malicious actor creates a chatbot, which impersonates a trusted entity like a bank or tech support to trick people into revealing sensitive information.
- An employee is targeted by a scammer who uses generative AI to create an SMS message to impersonate the CEO of the company. The scammer uses the fake message to instruct the employee to transfer funds to a fraudulent account.
- A threat actor uses HR policy announcements and benefits updates to lure victims and steal employees’ credentials.
- Cybercriminal uses generative AI to create convincing fake social media profiles that can be used to impersonate real people or organizations.
- Attackers send text messages to social engineer a victim within an organization into giving valuable financial information or data.
- A threat actor uses AI to automate certain aspects of cyberattacks, such as generating malicious payloads or evading security systems.
- AI is used to analyze large amounts of data to identify vulnerabilities or find targets for attacks.
As mentioned above, the types of attack vectors that will be most impacted will be social engineering attacks like BEC and ransomware threats. Cyberattacks are most dangerous when delivered with speed and frequency to specific targets in an organization. With malware, ChatGPT enables cybercriminals to make an infinite number of code variations to stay one step ahead of the malware detection engines.
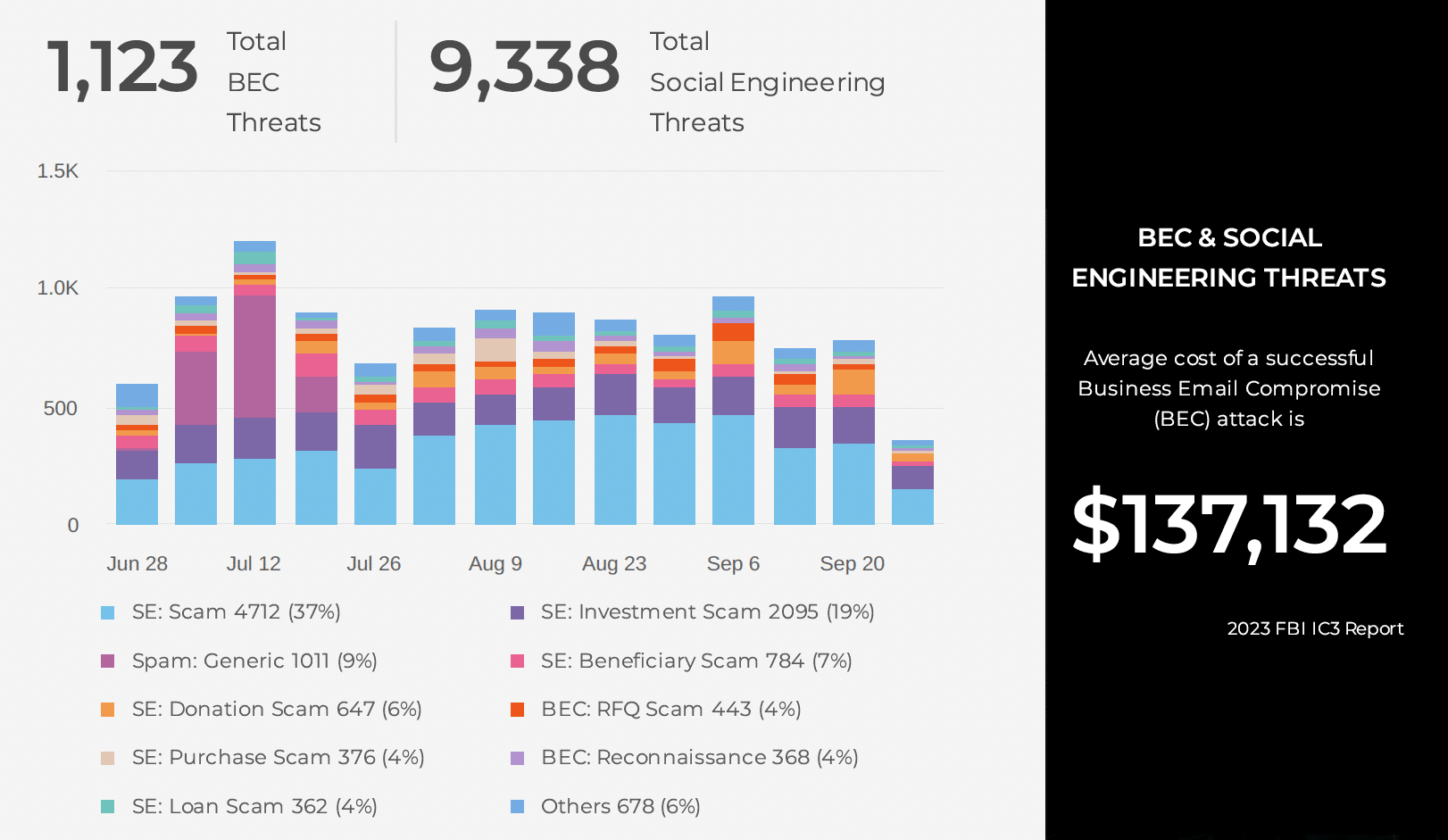
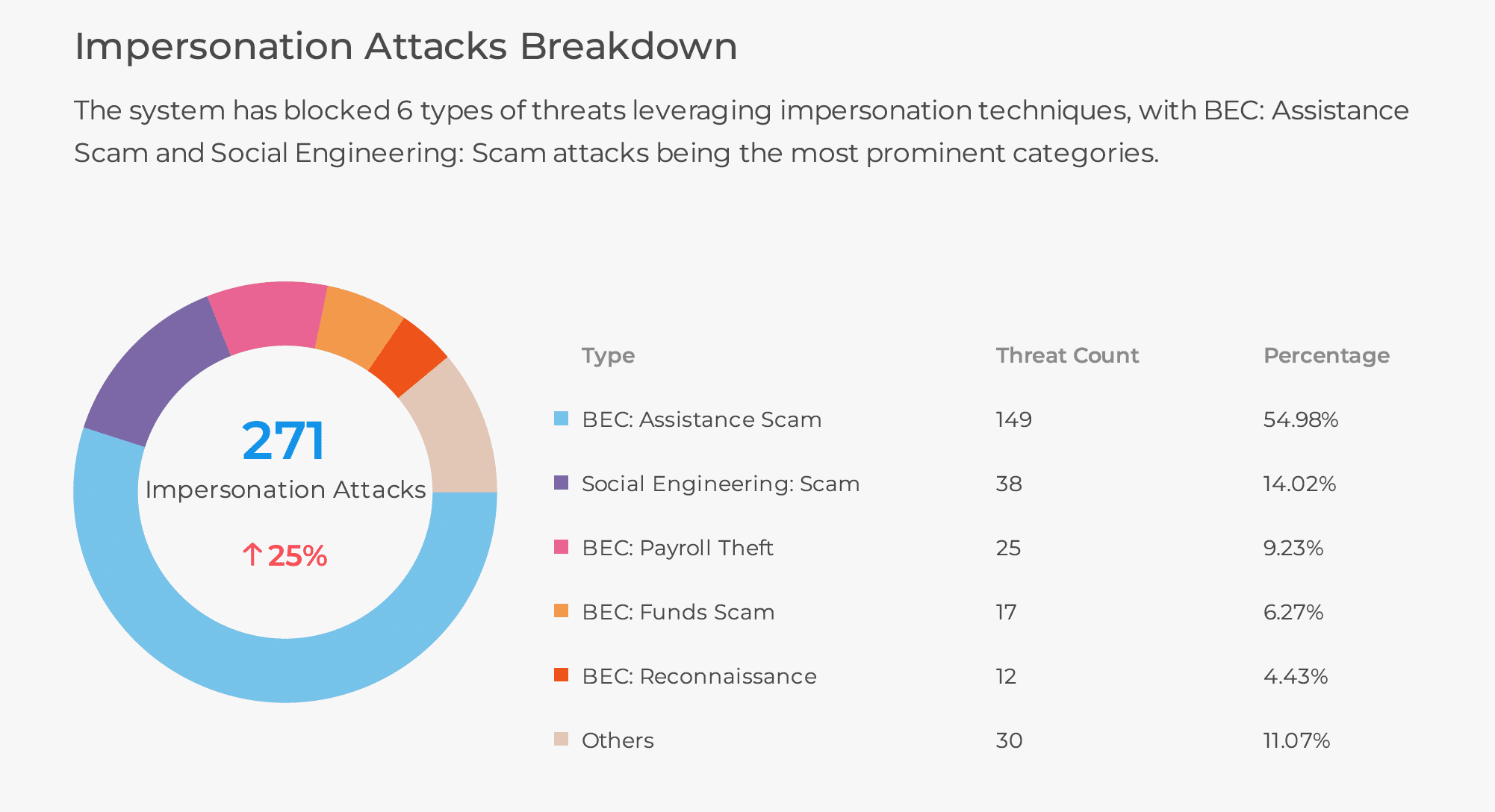
It’s important to note that the threat of ChatGPT is real today, particularly with malware and BEC threats! Business Email Compromise attacks are targeted attempts to social engineer a victim into giving valuable financial information or data. These attacks require personalized messages delivered to targeted organizations to be successful, and ChatGPT can now create well-written personal emails en-masse with infinite variations, making this method of cyberattacks dangerous to victimized organizations.
The speed and frequency of these attacks will increase and yield a higher success rate of user compromises and breaches. Legacy security technology doesn’t stand a chance against these types of attacks.
It’s important to realize that you must fight AI cyberthreats with AI cybersecurity technology or you’ll lose. Many organizations are not prepared for how this is going to change the threat landscape. We can no longer rely solely on the naked eye or human intuition to solve complex machine-generated security problems.
The abuse of AI is something we at SlashNext knew would happen for a long time, which is why SlashNext has been developing natural-language generative AI technology for a year and a half in anticipation of these types of threats.
Generative AI technologies can predict millions of new variants of the threats that might enter an organization, and this is the only way to counteract these AI attacks to close the security gap and vulnerabilities created by this dangerous trend.
We know that 82 percent of breaches involve a human element. To combat this, we created a patented technology – called HumanAI™ – that adds augmented AI and behavioral contextualization to computer vision and natural language processing (NLP) to detect BEC in email and mobile with unprecedented predictability. SlashNext integrated cloud email and messaging security stops BEC, smishing, account takeovers, scams, phishing attacks and more.
It fights machine with machine!
For more information and the stages of a BEC attack, check out our page on Business Email Compromise.
To see a personalized demo and learn how our product stops zero-hour credential stealing, BEC, spear phishing, social engineering, ransomware, and more, click to schedule a demo or easily test the efficacy of your current email security as well with no impact to your existing email infrastructure using our 5-min setup Observability Mode!