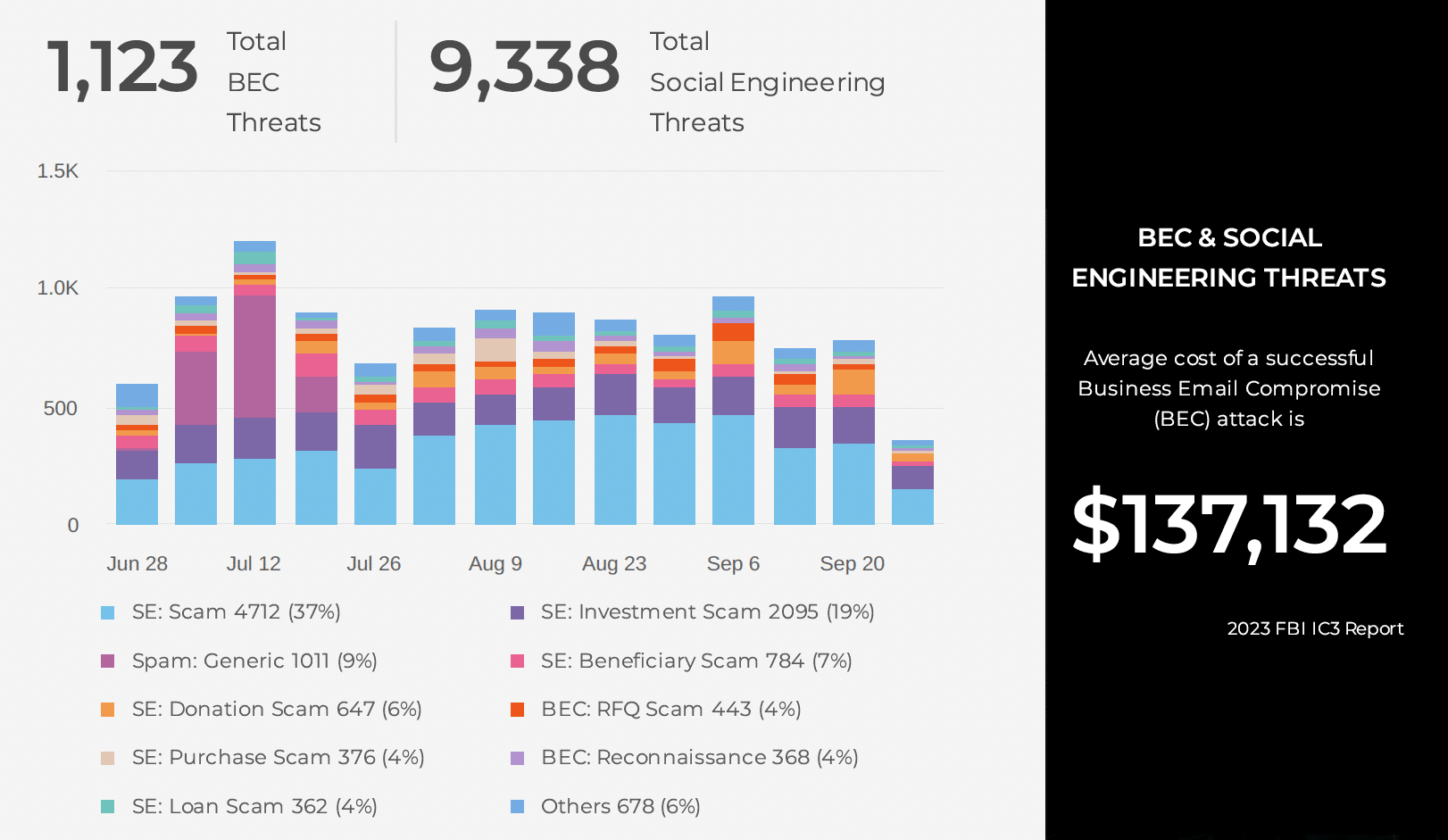
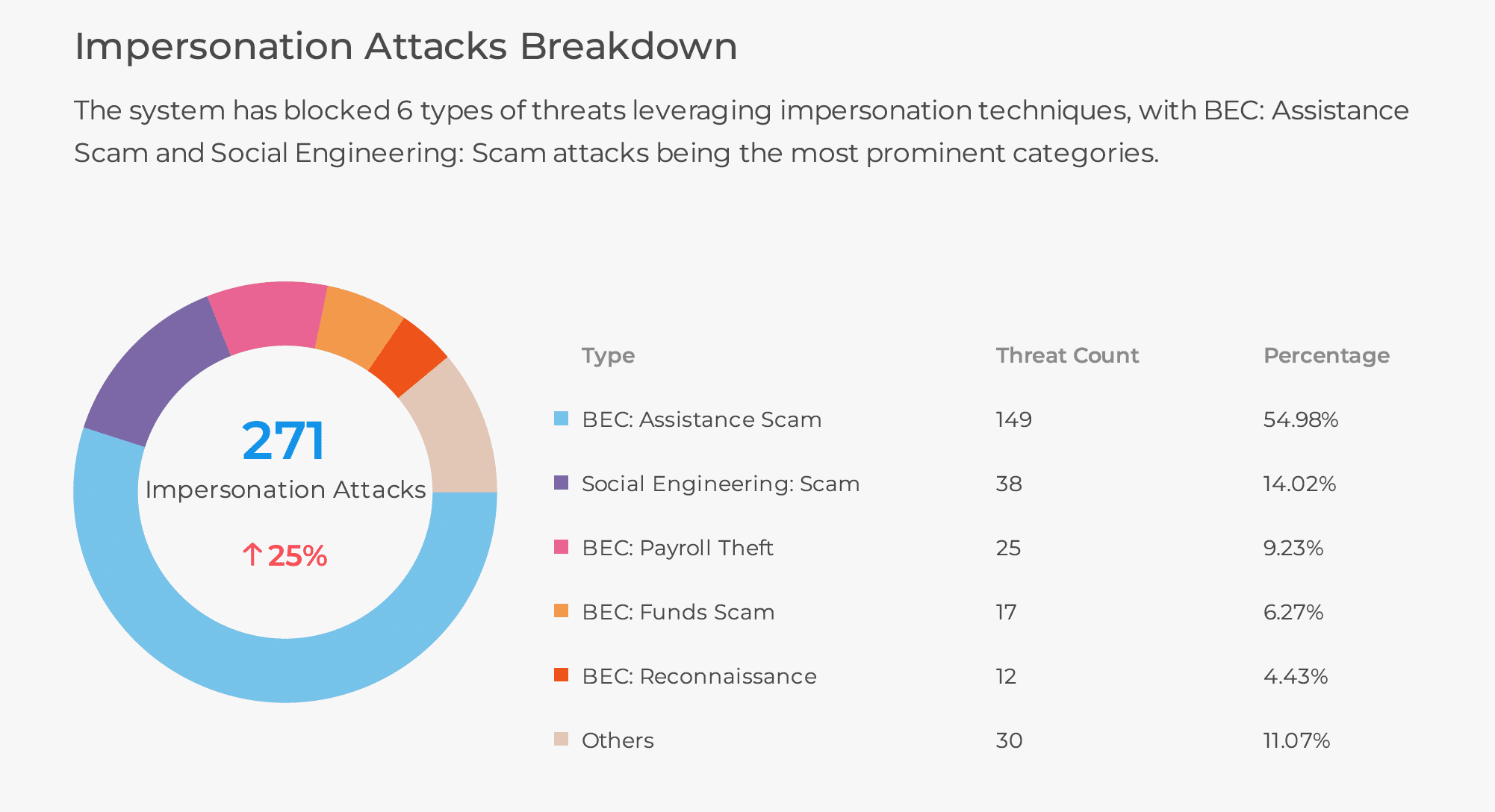
Credential phishing is a type of cyberattack where attackers attempt to deceive your employees into providing their sensitive information, such as their Microsoft usernames and passwords. What is not obvious is credential phishing is the root cause of many breaches, including the recent ransomware breach at UnitedHealth subsidiary Change Healthcare. According to UnitedHealth Group CEO Andrew Witty, criminals used compromised credentials to remotely access a Change Healthcare portal, an application used to enable remote access to desktops. Once the threat actor gained access, they moved laterally and ultimately deployed ransomware that resulted in a $22M ransom payout.
It is unknown how the cybercriminals got hold of the credentials used in the attack; however, it is commonly achieved through credential phishing emails. In this blog, I will explore how our Gen AI Email+ Security Service proactively scrutinizes URLs embedded within credential phishing emails.
Live Scan Using Virtual Browsers and Machine Learning
Live Scan™ harnesses the power of virtual browsers and computer vision machine learning (ML) classifiers. Virtual browsers serve as our first defense line, emulating the behavior of web browsers to access email URLs. For example, how you open email URLs in your Safari or Chrome browsers. This is important because credential phishing webpages are social engineering attacks that attempt to make you believe you are looking at the real Microsoft login page.
Virtual browsers enable our service to see what is visually presented to the user. Virtual browsers also enable the service to overcome defensive measures like CAPTCHA and Cloudflare’s Turnstile service, which are implemented by attackers to prevent their webpages from being scanned. These attacker defensive measures are becoming increasingly more common.
Once the webpage is fully rendered in the virtual browser, computer vision is applied to the webpage content and visual elements are scrutinized for visual deviations, including layouts, logos, and textual content. What sets the SlashNext computer vision ML apart is the specificity of our classifiers, which are trained to identify webpages impersonating a wide array of applications – from enterprise platforms like Microsoft and Zoom to popular social media networks like Facebook and Twitter. This is crucial because many employees use the same passwords for their personal and work applications.
Lastly, Live Scan is applied to the link as well as QR and file-based credential phishing emails.
Final Thoughts
It is essential to recognize that there is no silver bullet solution. Phishing protection requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses technology upgrades, process improvements, and user awareness, which serve as strong prevention measures and become the cornerstone of an effective defense.
In a recent independent efficacy study, SlashNext Gen AI Email+ Security stopped 99 percent of zero-hour credential phishing attacks, more than 25 percent higher than the nearest competitor.
We invite you to reach out and discover how the SlashNext solution can fortify your organization against a spectrum of threats, including credential phishing, Business Email Compromise (BEC), and advanced phishing attacks.
To see how SlashNext can protect your organization from credential phishing and other types of email-based threats, schedule a demo today and experience the most advanced email security on the market.