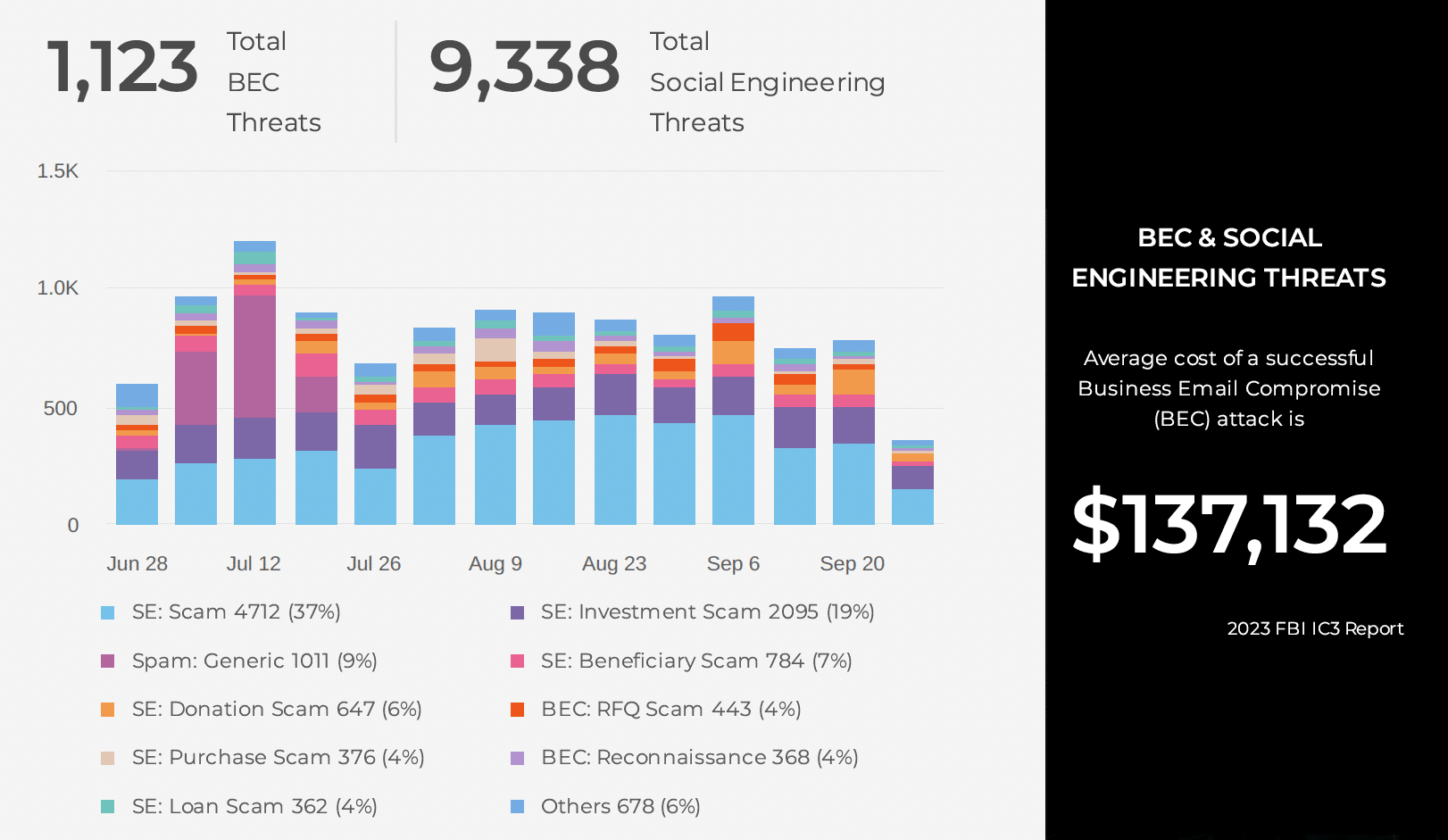
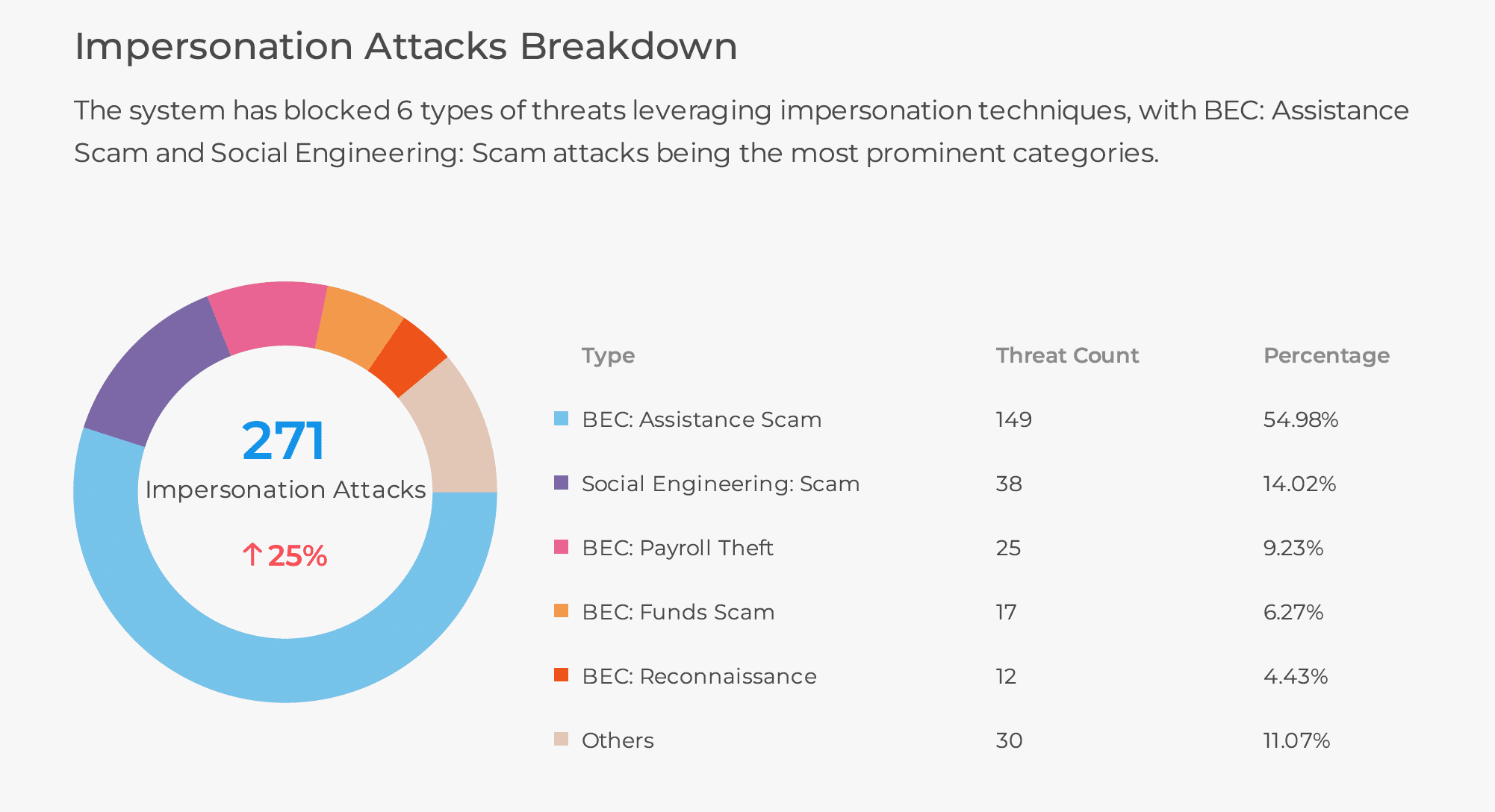
What type of phishing became very effective around 2010 and still worries security teams today? Spear phishing. Spear phishing remains highly effective and is getting more dangerous by the day. What is spear phishing? What new technologies and methods will attackers use to get around common defenses? How will they become more precise and convincing? We will explore these questions below.
What Exactly Is Spear Phishing?
Spear phishing is a targeted attack that uses detailed information about a victim. It creates personalized emails or messages. The goal is to trick the person into sharing sensitive information or taking certain actions.
Spear phishing, in contrast to standard phishing, concentrates on specific victim information. Gaining the victim’s trust and successfully taking advantage of them is made easier with this information. Attackers are improving spear phishing by using tactics like voice and video scams. They also use QR code exploits, SMS phishing, and platform-based attacks.
Learn about five new spear phishing tactics that are growing on the dark web. Find out how attackers are changing spear phishing to use new technology trends.
1) Platform Diversification
Spear phishing isn’t just about email anymore. Attackers are now targeting individuals through platforms like Microsoft Teams, LinkedIn, WhatsApp and others.
These channels let them create personalized interactions. This helps them avoid typical email security measures. As a result, their attacks are harder to detect and more effective.
Lazarus attackers, for example, ran an operation called Operation Dream Job. They impersonated recruiters on LinkedIn to target their victims. After establishing rapport, they sent malicious links with an executable quiz to download.
Now, in 2024, they are reaching out via LinkedIn and WhatsApp with links disguised as job application forms. These links lead victims to phishing sites designed to steal login credentials and personal information.
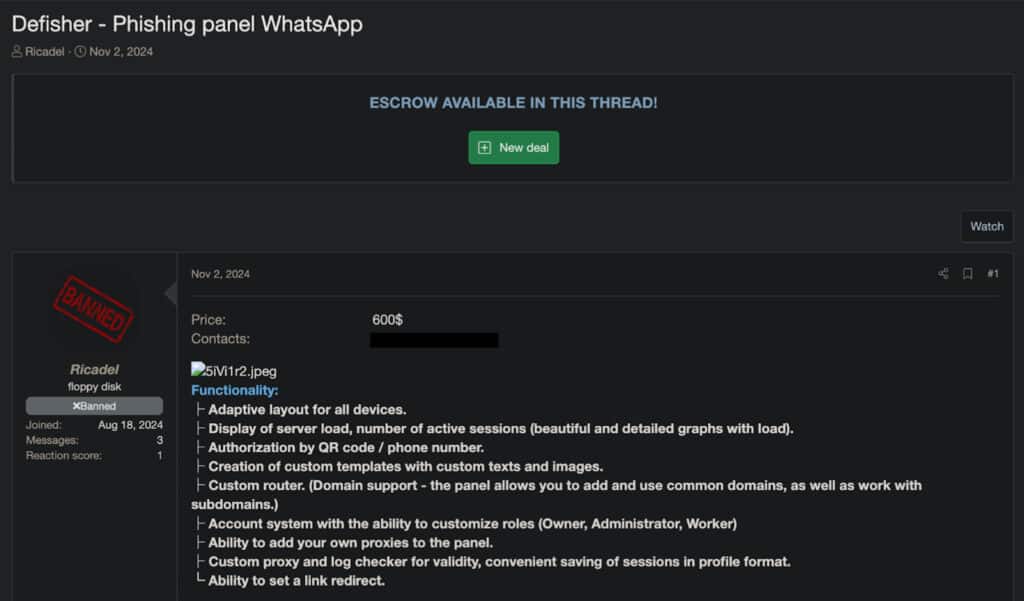
Example of a phishing tool for WhatsApp
In workplace scenarios, collaboration tools like Microsoft Teams have become a big target. Victims, who often rely on these tools in their daily work, are more likely to engage with an attacker. They do this without any real suspicion. When attackers use different platforms, it makes security tools less effective. This makes it harder for users to spot real messages and get rid of malicious ones.
2) Voice and Video Fakes
Deepfake technology has taken spear phishing to a whole new level. Attackers can now create incredibly realistic voice and video impersonations, tricking people into doing things like transferring money or giving away sensitive information. It’s harder than ever to tell what’s real and what’s fake.
A recent case in Hong Kong shows how convincing scams can be. It started with an email and led to a video call. A finance worker was tricked into transferring $25 million. The scammer looked and sounded just like their CFO. The deepfake was so realistic that the fraudulent request seemed completely legitimate.
A tool being shared on a cybercrime forum for voice impersonation
On cybercrime forums, deepfake creation services are readily available, enabling attackers to generate these impersonations at low cost. For as little as $10, attackers can purchase tools to replicate a victim’s voice or image.
These fakes are often delivered through spear phishing emails or messages to make the request seem even more convincing. For example, an attacker might send an email that looks like it’s from an executive. They may then follow up with a deepfake voice message. This message pushes the recipient to act on the "urgent" request.
3) QR Code Spear Phishing
QR codes are everywhere. They are now used in spear phishing attacks to secretly deliver malicious links and files. QR codes obscure their destination from view. This makes it easier for attackers to trick and exploit victims who are not careful about scanning them.
Cybercriminals discussing ways to exploit QR codes
Unlike generic phishing campaigns, QR code spear phishing targets specific people or groups. This can include employees of a certain company or attendees at an event. Attackers can, for example, embed malicious QR codes in event materials or company presentations. These codes can lead victims to phishing pages that look like internal login portals.
4) Phishing-as-a-Service (PhaaS)
Spear phishing attacks are being built out using pre-made tools and services offered by phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platforms. They offer customized phishing websites, real time credential collection interfaces and even features to intercept one time passwords (OTP).
In an example we found on a cybercrime forum, a seller promoted a phishing panel. This panel could target email services like Gmail, Outlook, and ProtonMail.
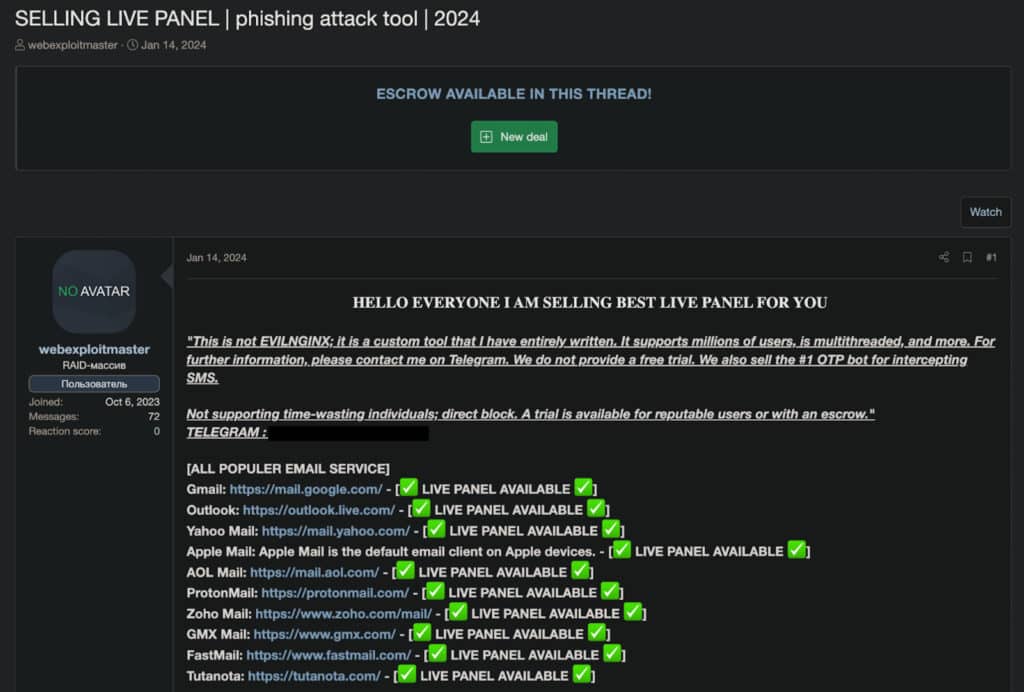
A ready-made phishing set-up tool
The service offered multithreading and support for personalized campaigns. This allowed attackers to expand their operations while still targeting individual users. These capabilities make it easier for attackers to launch spear phishing campaigns. PhaaS lowers the barrier of entry for them.
5) SMS Gateways for Targeted Smishing
Smishing is often linked to large phishing scams. However, cybercriminals are now using advanced SMS gateways for targeted spear phishing attacks.
These gateways allow the delivery of personalized messages. These messages appear to come from reputable sources, like financial institutions, healthcare groups, or employers. This can happen through spoofed phone numbers, for example.
Example of a SMS gateway used in smishing attacks
For example, an attacker might send an SMS pretending to be from a victim’s bank. The message warns about suspicious activity in the victim’s account. The message includes a link to a phishing site that mimics the bank’s login page, prompting the victim to enter their credentials.
This example may seem like a typical phishing attack; however, cybercriminals often use this method to target wealthy individuals. This makes it a more focused spear-phishing situation.
Secure Your Team from Spear Phishing
Email is no longer the only way to spear phish. Attackers are now exploiting platforms like LinkedIn, WhatsApp, and Teams. They are also using deepfake technology and QR code exploits to bypass traditional defenses.
Advanced AI-driven threat detection is used by SlashNext to identify and block these methods in real time. Our solutions detect novel threats by analyzing context, behavior, and communication patterns across multiple channels.
Stay ahead with us and learn more at SlashNext.com about spear phishing. Learn how we address these challenging techniques by filling out the contact form.