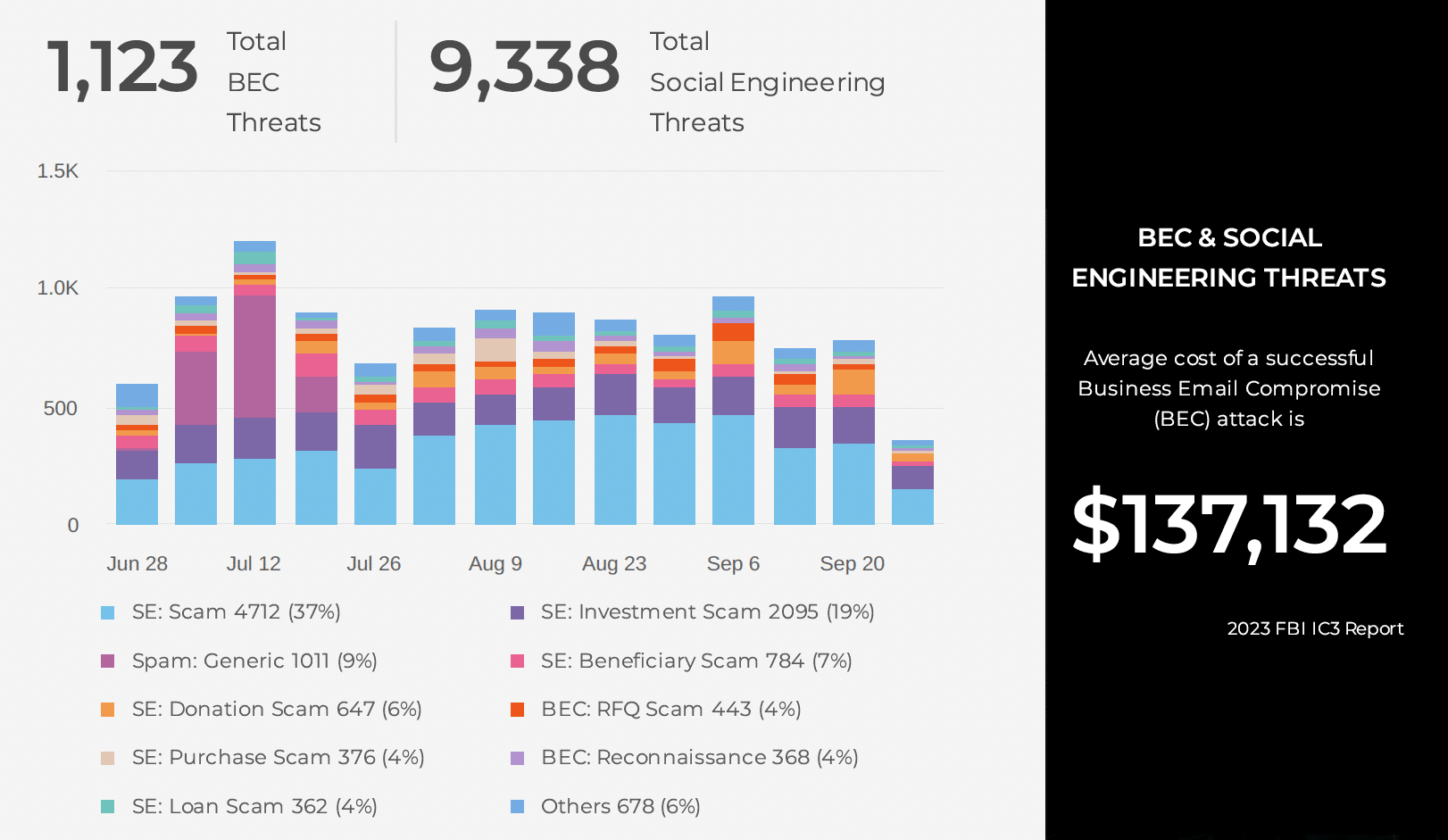
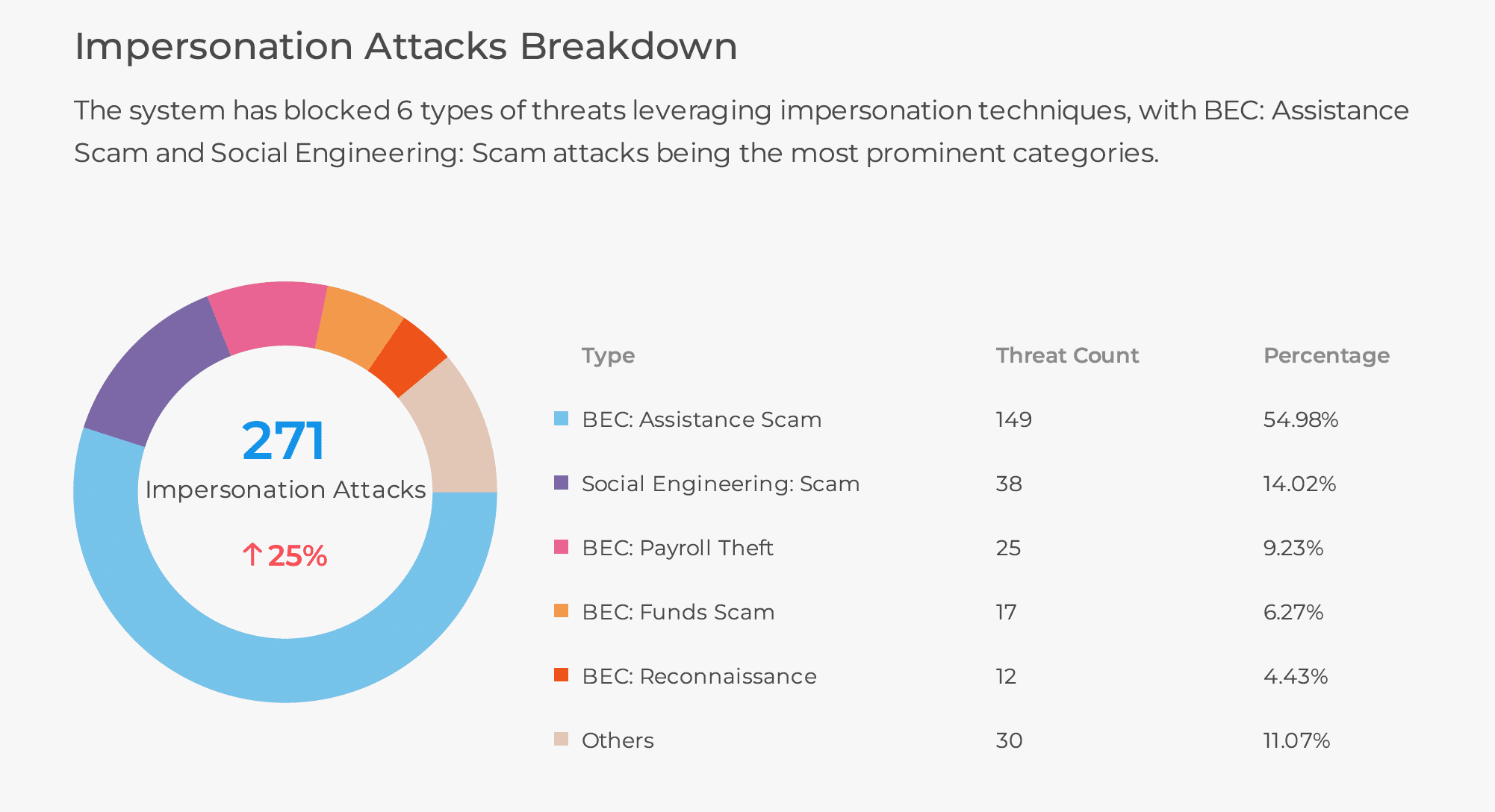
With the demands of the modern workforce, there’s been an increased use of native cloud email protection, like Microsoft 365, in the last 12 months. This has led many security professionals to ask if Microsoft 365 Defender can provide enough threat coverage to protect their organization. They wonder if they need advanced detection such as computer vision machine learning against phishing threats and other highly targeted threats, and what tools are required beyond Microsoft Defender to keep users safe?
Why You Need Advanced Phishing Detection to Protect Email Users
Email is an important communication channel for professional and personal use. With our world being a remote work-from-anywhere on any device workforce, people use the same devices for personal and professional use. At the same time, email threats have become advanced, and signature-based detection struggles to stop these threats from today’s cyber criminals. Microsoft’s built-in security can detect and stop known threats. It struggles with zero-hour threats, spear-phishing, threats from trusted services, ransomware, and other complex phishing attacks.
The Rise in Advanced Phishing Threats
The rise of well-crafted spear phishing is the leading factor in the success of phishing attacks and ransomware. Spear-phishing delivered through trusted cloud services bypass traditional cybersecurity solutions at an alarming rate. In the first half of 2022, SlashNext reported that 80% of phishing emails detected had URLs hosted on trusted services.
Let’s take a look at the different types of advanced threats.
Spear-phishing
While phishing used to be mass emails try to encourage someone to do something, including downloading a malicious attachment, clicking through to a compromised website, or completing a credential harvesting form, spear-phishing is just like it sounds, targeted with a message specifically aimed at one person. By design, these attacks are personalized to encourage the user act. In all these cases, the user is compromised, which could lead to a data breach. These types of threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated as emails and websites are designed to look more like established and trusted brands. Here are five steps of how a spear-phishing attack happens:
- The Attacker focuses on a specific high-value target. The Attacker then uses data from social networks and the dark web.
- Meticulously crafted bait is then used against the user. The attacker then obtains the user’s credentials for deeper attacks against bigger targets or used for data exfiltration, ransomware, backdoors, and malware infections
Trusted Service Compromise
With a work-from-anywhere environment, employees have started using different channels and services to stay connected, contactable, and informed. Users blindly trust that these channels, like email, that we use all day, every day, are protecting us against cyber criminals and their tactics. Unfortunately, that’s not always the case.
Cybercriminals have adjusted to the new remote workforce and wisely know how we communicate and share information. Services like Slack, SharePoint, Outlook, LinkedIn, Microsoft 365, and others are all susceptible to trusted service compromise. These domains’ trusted reputation enables cybercriminals to easily evade current detection technologies using domain reputation and blocklists like SEG, proxy, SASE, and endpoint security tools. It’s important to understand how these cyber criminals gain access to legitimate hosted domains. One popular tactic is account takeover. Once a cybercriminal has access to Microsoft 365 credentials from one company, they can initiate attacks against other companies, and those targets will have a sense of trust. Using mainstream, legitimate commercial infrastructure sites to avoid detection has been a successful tactic, and the growth in these threats continues in 2022.
Ransomware
Ransomware is a threat via email. It uses software to block access to files usually containing important intellectual property, sensitive data, or other important information that a user or business values. This information cannot be accessed until you pay a ransom to the cybercriminal. The average cost of a ransomware attack is over $4 million. That is a lot of money at risk.
When it comes to ransomware attacks, it’s important to understand how pervasive the risk is to businesses. Ransomware has continued its upward trend with an almost 13% increase–a rise as big as the last five years combined, according to Verizon 2022 DBIR (Data Breach Investigations Report). The human element contributes to 82% of breaches, and stolen credentials provide a great second step in an attack.
Microsoft Defender, Integrated Cloud Email Security, and Secure Email Gateway
According to Gartner, 70% of organizations use cloud email solutions, but complexity and security continue to concern organizations. Zero-hour Spear phishing and threats on trusted services can slip past secure email gateways because domain reputation detection, URL rewriting, and trust graphs cannot detect complex phishing threats. Integrated Cloud Email Supplements (ICES) help fill in the gaps and work with services like MS Defender to provide layered protection against all types of threats.
As a partner with Microsoft, you’ll be fully protected with SlashNext Email Protection for Microsoft 365. SlashNext AI-powered behavioral analysis and LiveScan is a purpose-built ICES for Microsoft 365 to stop zero-hour attacks missed by Microsoft email security specifically. Protect users from targeted credential stealing, supply chain threats, spear-phishing, trusted service compromise, social engineering scams, ransomware, and malware link threats that elude other security solutions up to 65% of the time, according to Tolly Group independent testing. This is the next step in protecting your organization from today’s and tomorrow’s cyber threats.
SlashNext AI-powered detection and LiveScan™ see through evasion tactics and detect previously unknown, zero-hour threats, including compromised websites and trusted hosting services, shortened links, multiple redirects, and other types of obfuscation. This is where Integrated Cloud Email Supplements come into play.
Read our latest white paper, Microsoft 365 + Integrated Cloud Email Security, Transitioning from a Secure Email Gateway to Modern Architecture for the Modern Enterprise, for a detailed look at these questions with answers on securing cloud email services against threats. See SlashNext live and in action here.