
Stopping Sophisticated Social Engineering Scams – Looking Beyond the Basic Signs
Most social engineering attack signs are really indicators for basic attacks from less experienced and sophisticated hackers. Today’s attacks are more sophisticated.
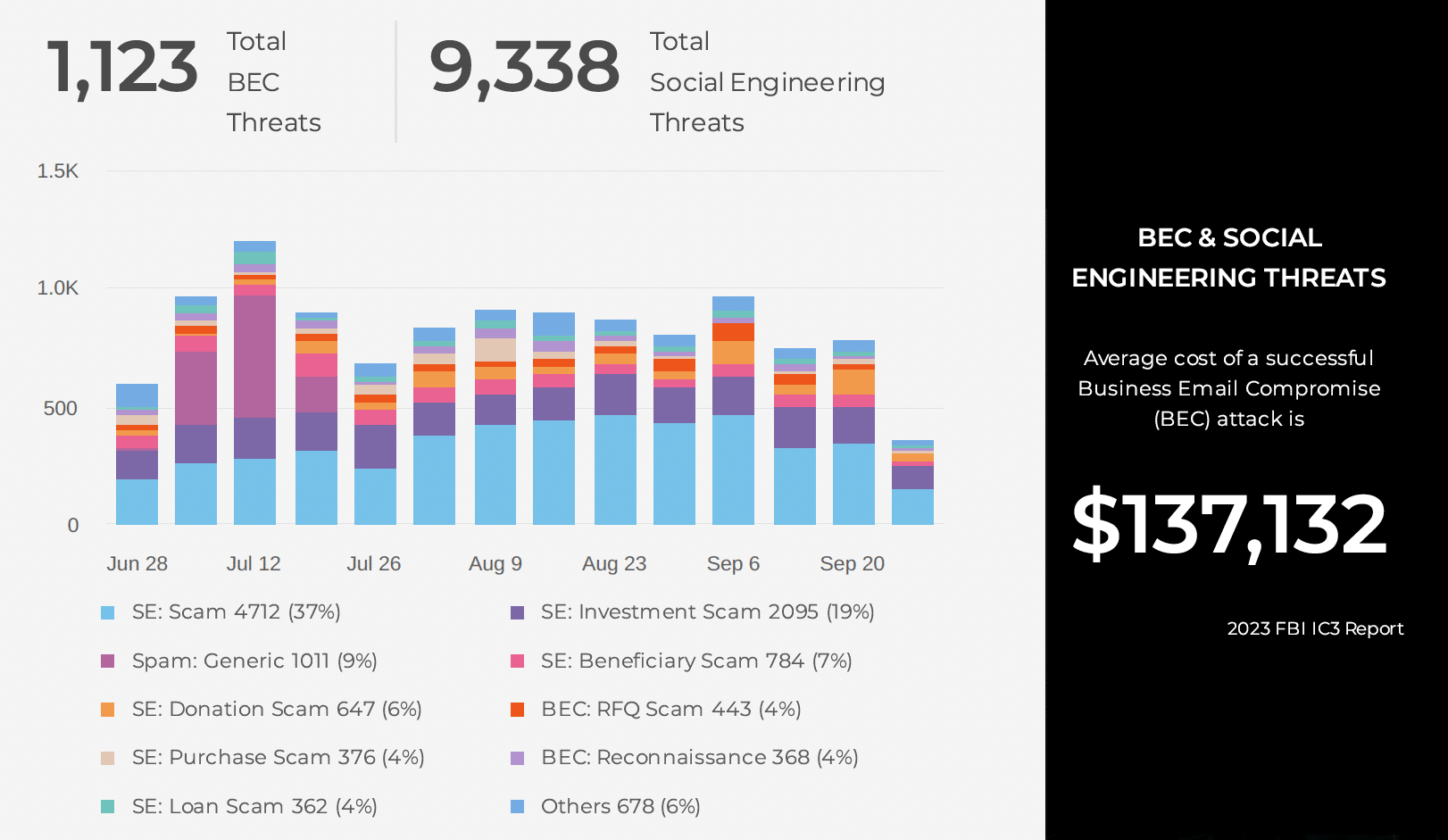
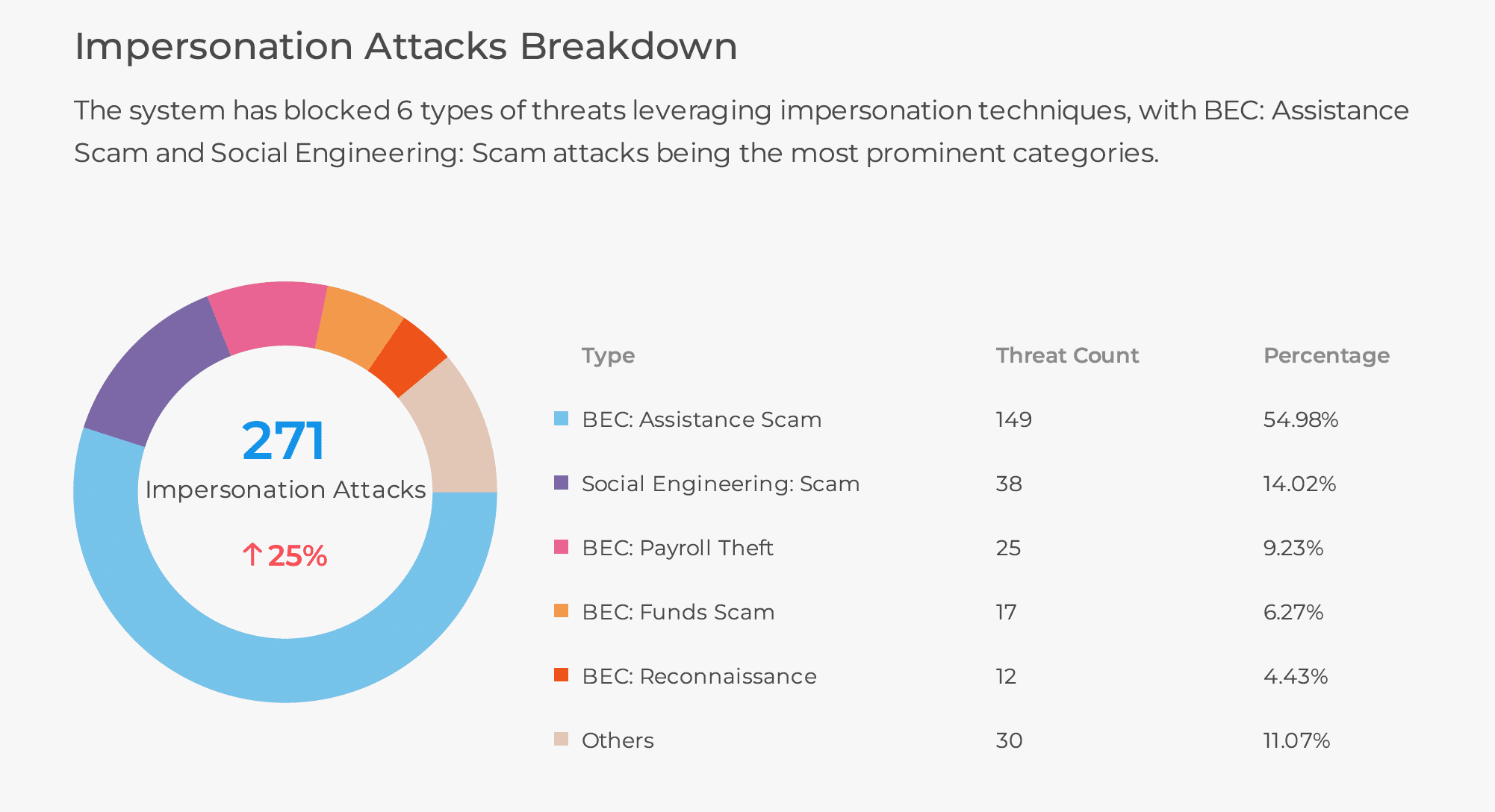


Most social engineering attack signs are really indicators for basic attacks from less experienced and sophisticated hackers. Today’s attacks are more sophisticated.

Today SOC teams seem to be in a state of flux; where balancing the need for fast, threat remediation is challenged by the volume of threats. Here are some thoughts.

SlashNext recently discovered a new malicious phishing threat that abuses Adobe’s open redirect services. Read our blog for details and how you can stop it.

New research found that Microsoft Office 365 ATP takes up 250 days to create phishing attack signatures. Here’s what users can do.

Here are six evasive phishing tactics that are getting around traditional cybersecurity protocols and how you can stop them.

Osterman Research believes automating incident response and detailed security policies should be part of any holistic approach to threat prevention. They identified 8 musts to include.

As bad actors become more sophisticated in their cyber-attacks, so too have their success in gaining access to corporate data, financial assets, and networks. Here are 7 growing threats.

Being able to block employee web traffic to phishing sites and stop a ransomware attack at the start of the kill chain, is paramount.

Just how prevalent are these phishing callbacks and C2 infections? In every client install we perform – 100 percent! – we see C2 infections and callbacks. Are you compromised?

SlashNext has partnered with ThreatQuotient to integrate SlashNext Real-Time Phishing Threat Intelligence with the ThreatQ platform. Read our blog for details.